High-Level System Design for URL Shortener Service
Tiny URL
This document outlines the design of a URL shortener service that creates an alias with shorter length, when browsed with short URL it would redirect to original URL.
Long URL: https://cloudaficionado.substack.com/p/d2741707-01a7-4064-ac33-09ed7ff7ab32
Short URL : https://tinyurl.com/3sh2ps6v
System Requirements
Shorten URLs: Generate unique short aliases for long URLs.
Redirect Requests: When a user visits a short URL, redirect them to the corresponding long URL using a 301 (permanent) redirect.
Scalability: Handle a high volume of URL shortening and redirection requests.
Availability: Ensure high uptime and minimal downtime.
Back-of-the-Envelope Estimation
Write Operations: Estimated at 1160 requests per second (100 million URLs per day). Assuming 100 million URL's are generated per day, 10^8/24/3600 = 1160 requests per second.
Read Operations: Estimated at 11600 requests per second (assuming 10 reads per long URL).
Storage: Estimated at 365 TB (365 billion URLs, 100 bytes per URL and metadata).Assuming this service runs for 10 years = 100 million * 365 * 10 = 365 billion URL's.
API Design
Shorten URL API:
Method: POST
Endpoint:
/api/v1/data/shortenRequest Body: Contains the long URL to be shortened.
Response: Returns the generated short URL.
Redirect API:
Method: GET
Endpoint:
/api/v1/shortUrlRequest Parameter: Short URL.
Response: Performs a 301 redirect to the corresponding long URL.
URL Redirection
The server intercepts requests for short URLs.
It retrieves the associated long URL from the database.
The server issues a 301 (permanent) redirect response to the user's browser, directing them to the long URL.
Difference between 301 and 302 redirect is -
302 redirect states that a URL is temporary moved and a request for long URL will go to shortener service.
301 redirect states that a URL is permanently moved to new URL which will be cached and subsequent request will be forwarded to cache. It would reduce the read request to service.
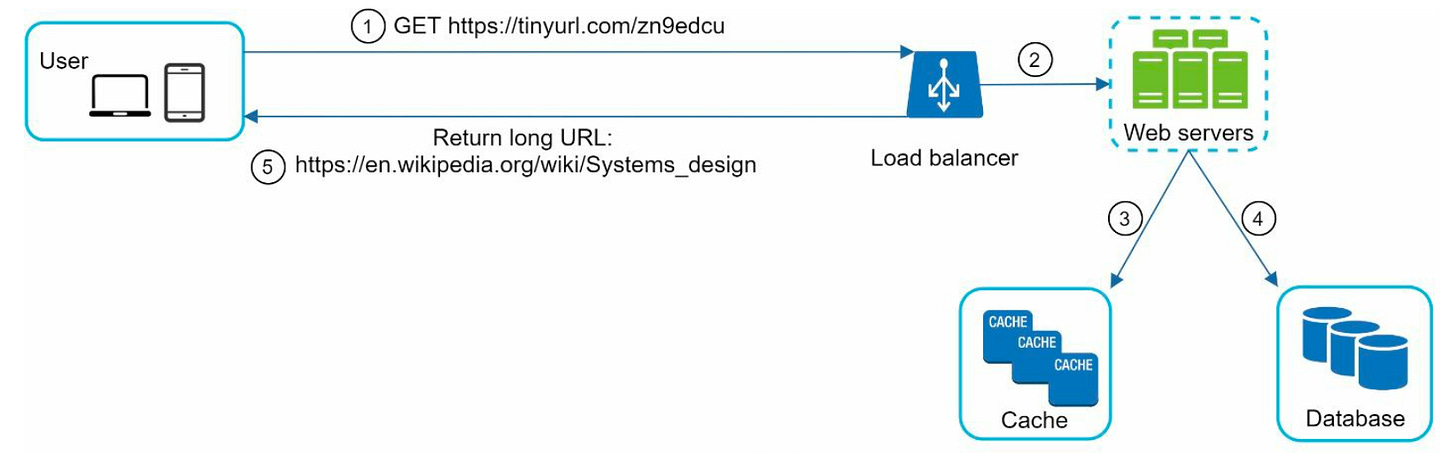
System Design
We would persist an unique id, short URL and a long URL in a distributed database. When user requests for a long URL it goes to web server which checks in cache if it exists return else it would go to database to fetch long URL
Short URL Generation Approaches
Hashing:
In this approach, we would use a hash function to convert a value of long url to short url, hash value would consist of 62 possible characters [0-9,a-z,A-Z].
Length of hash value is 62^n >= 365 billion, as we need to support 365 billion urls. 62^7 = 3.5 trillion which is enough to support our estimate.
We would implement a hash function that hashes a long URL to 7 characters, we can use hash functions like MD5 or SHA1 but their hash value is too long. To make it shorter we can consider only first 7 characters but that could lead to hash collision. To resolve this collision we can append a constant string to long URL and hash again until no more collision is found.
To check efficiently if a hashed short URL exists, we can use bloom filters, if it exists this means there is a collision.
Base62 Encoding:
We can use bas 62 conversion as there are 62 possible characters [0-9,a-z,A-Z] for a hash value. we would use a unique id generator here. we would be calculating the base 62 value of this unique id to use it as short URL.
when a long URL is passed as input it checks if long URL is in database, if it is fetch short URL and return.
If long URL is new, generate a unique id and convert this id to short URL with base 62 conversion and persist in database.
Offers better collision resistance compared to truncated hashing.
Unique id generator :
UUID is a easy way to obtain unique ID's, which is a 128 bit number considering it's length it won't be duplicate. It can be generated independently in each web server without any coordination between servers and it would still be unique.
Another format which could be used to generate unique id is <signedbit>_<timestamp>_<datacenterid>_<machineid>_<seqno>.
Wrap-Up
The web server acts as a stateless service for generating unique IDs, short URLs, and persisting them in the database.
Enabled Caching to access frequently accessed mappings (short to long URL) for faster lookups.
The database layer utilizes replication and sharding with consistent hashing for scalability and high availability.
UUID generator is needed to persist the URL’s uniquely in database, and is needed in case of base 62 encoding approach as we encode uniqueid as a short URL.